Telemedicine, the provision of healthcare services remotely through technology, has emerged as a critical tool in bridging the healthcare divide, especially in rural areas where access to medical care can be challenging. This article explores the effectiveness of telemedicine services in addressing healthcare needs in rural communities.
The Challenges of Healthcare in Rural Areas:
Rural communities often face significant challenges in accessing healthcare services. Limited availability of healthcare facilities, long distances to medical centers, and a shortage of healthcare professionals are common issues. These challenges contribute to delayed diagnoses, poorer health outcomes, and higher healthcare costs for rural residents.
How Telemedicine Works:
Telemedicine utilizes telecommunications technology to facilitate healthcare delivery remotely. It allows healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients from a distance using video conferencing, mobile apps, and other digital tools. This approach eliminates the need for in-person visits and can significantly reduce travel time and costs for patients.
Benefits of Telemedicine in Rural Settings:
Improved Access to Specialists: Telemedicine enables rural patients to consult with specialists located in urban areas without traveling long distances.
Timely Care: Remote consultations allow for quicker access to medical advice and intervention, potentially reducing the risk of complications from untreated conditions.
Cost Savings: By reducing travel expenses and time away from work, telemedicine helps lower overall healthcare costs for rural patients.
Continuity of Care: Patients can receive ongoing monitoring and follow-up care remotely, ensuring continuity in their treatment plans.
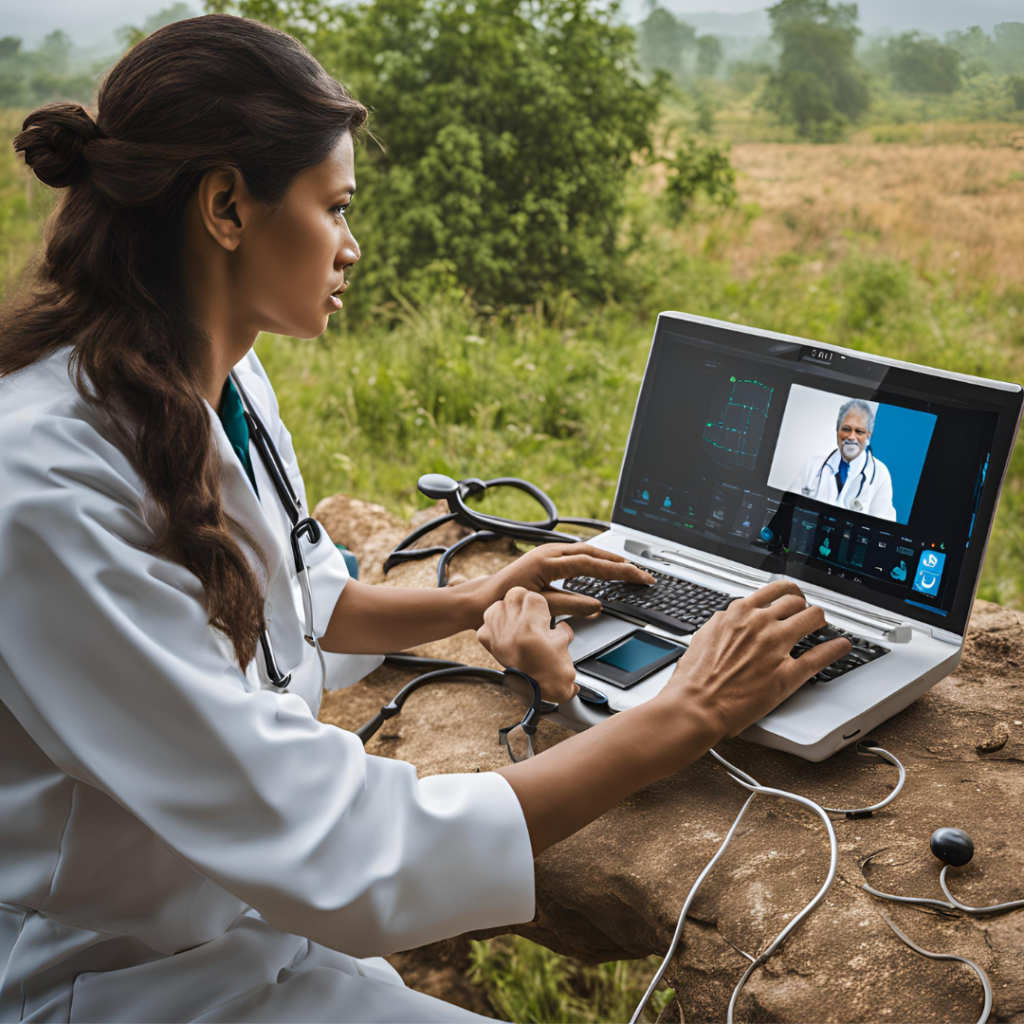

Case Studies and Success Stories:
Numerous studies have highlighted the positive impact of telemedicine in rural healthcare. For example, a study conducted in [specific rural area] found that telemedicine reduced emergency room visits by [percentage], demonstrating its effectiveness in managing chronic conditions remotely.
Challenges and Considerations:
While telemedicine offers promising benefits, several challenges must be addressed for widespread adoption in rural areas:
Technological Barriers: Limited internet connectivity and technological literacy can hinder access to telemedicine services.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues: Reimbursement policies and state regulations may vary, affecting the availability and affordability of telemedicine services.
Privacy and Security Concerns: Protecting patient information during remote consultations is crucial and requires robust security measures.
Telemedicine represents a transformative approach to healthcare delivery in rural areas, offering a viable solution to overcome geographical barriers and improve access to quality care. As technology continues to advance and healthcare policies evolve, telemedicine has the potential to become a cornerstone of rural healthcare systems, ensuring that all individuals, regardless of location, can access timely and effective medical services.
FAQs About Telemedicine Services in Rural Areas
1. What is telemedicine? Telemedicine refers to the remote delivery of healthcare services using telecommunications technology. It allows patients to consult with healthcare providers via video conferencing, mobile apps, or other digital platforms without needing to visit a medical facility in person.
2. How effective is telemedicine in rural areas? Telemedicine has proven highly effective in rural areas by improving access to healthcare services, reducing travel time and costs, and facilitating timely medical interventions. Studies show that it can lead to better health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
3. What healthcare services can be provided through telemedicine? Telemedicine can support a wide range of healthcare services, including primary care consultations, mental health counseling, chronic disease management, follow-up visits, and specialist consultations.
4. Are there any limitations to telemedicine in rural settings? Telemedicine may face challenges in rural areas due to limited internet connectivity, technological infrastructure, and regulatory barriers. Additionally, some medical conditions may still require in-person examinations or procedures.
5. How can patients access telemedicine services in rural communities? Patients in rural areas can access telemedicine services through healthcare providers that offer telehealth options. This may include local clinics, hospitals, or specialized telemedicine platforms that connect patients with healthcare professionals remotely.
6. Is telemedicine covered by insurance in rural areas? Insurance coverage for telemedicine services varies by provider and location. Many insurance plans now include coverage for telehealth visits, but it’s essential for patients to check with their insurance carrier to understand their specific coverage options.
7. What are the privacy considerations with telemedicine? Telemedicine platforms adhere to strict privacy and security standards to protect patient information during remote consultations. Healthcare providers use encrypted communication channels and secure platforms to ensure patient confidentiality.
8. How can healthcare providers in rural areas integrate telemedicine into their practices? Healthcare providers can integrate telemedicine by adopting telehealth technology, training staff on its use, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and educating patients about telehealth options available to them.
9. How does telemedicine contribute to healthcare accessibility in underserved rural communities? Telemedicine helps bridge the gap in healthcare accessibility by allowing rural residents to access timely medical care without traveling long distances. This can lead to earlier diagnoses, improved disease management, and reduced healthcare disparities.
10. What are the future prospects for telemedicine in rural healthcare? The future of telemedicine in rural healthcare looks promising with ongoing advancements in technology and policy support. As telehealth becomes more integrated into healthcare systems, it has the potential to enhance healthcare delivery, particularly in underserved rural areas.






Leave feedback about this